introduction
Today I will Explain How to Configure Replication With Replication type Transactional Replication then in another posts I will exaplain all Replication type and
How to manage the replication ,
how to manage the Replication Agent ,
How to monitor the replication ,
Hot to Check the Replication performance
Transactional Replication
in this Demo I install 2 virtual machine and 3 SQL Server instance
Virtual Machine : SQL-PC (Windows Server 2008R2 Enterprise Edition) With SQL Server (Default instance)
Virtual Machine : SQL2-PC (Windows Server 2008R2 Enterprise Edition) With SQL Server (Default instance , Named Instance = WitnessServer)
I will partition this Subject to three type :
1- How to install the Distribution Server. (SQL-PC)
2- How to install the Publication Server. (SQL-PC)
2- How to install the Subscription Server. (SQL2-PC)
How to install the Distribution Server
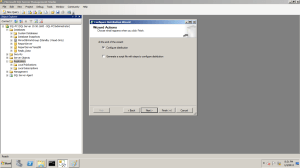
1- on machine Name SQL-PC open SQl Server Instance name SQL-PC Write Click on Replication then Select Configure Distribution
2- Select the Distributor Server : First option if you want SQL-PC is the Distributor Server .Second option if you won’t to Add another Distributor Server .
3- Enter the Snapshot Folder : in this Step Create Folder in make it Share then take the Network path of this Folder and put it in the Snapshot folder path
4- Create the distribution Database : this Database will be under the System Database like the master database
5- Select the Publisher Server : in this step you can add more than one Publisher Server but in my demo I will Add SQL-PC is publisher
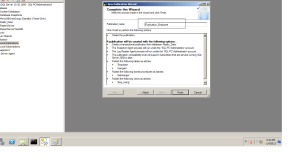
6- Finish the Configuration by Select between (Configure Wizard & Create T-SQL)
7-Configuration Distribution Complete successfully
8- Check the Distribution Database under the System Database
How to install the Publication Server
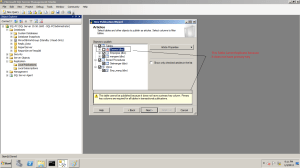
1- on machine Name SQL-PC open SQl Server Instance name SQL-PC Under Replication Select Load Publication the Wrote Click on it the Select New Publication
2-ٍSelect the publication Database
3- Select the Publication Type
4-Select the object to publish it (Table , View , Stored , other objects)
5- if you have table in this table don’t have Primary ley you can’t publish it like this table
6- if you won’t to add filter on this table
7- Configure the snapshot agent
8- Add the user for the Agent Security
9-Write Name to Publication
10- Check now your new Publication
How to install the Subscription Server
Now let’s to Connect to another Server (SQL2-PC) to install the Subscription on two Instance
- SQL2-PC
- SQL-PC\WitnessServer
1- under Replication Select Load Subscription
2- Selet the Publication Server
3- Select Server name to run the Agent (run on Distributor Server SQL_PC) or run it on Subscription Server
4- Select the Subscription Server and add the Subscription Database
5- Add another Subscription Server (SQL2-PC\WitnessServer
6- Configure the Distribution Agent Secuirty Add the User name Agent
7- Synchronize Schedule
8- ieinitialize Subscription
Now after this step you now finish the Configuration for SQL Server Transaction Replication .
Open SQL Server (SQL-PC) Publication then try to Edit any data in the Publication Database in table or View or Stored we Selected it on the Article and go to the Subscription Servers to Check this Data is transferred or no
Wait for me in another Replication posts
Regards ,
Mostafa Elmasry