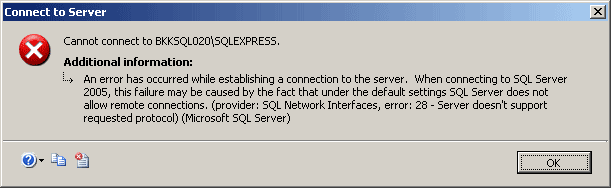
“Cannot connect to SQL-Server-Instance-Name
An error has occurred while establishing a connection to the server.
When connecting to SQL Server 2005, this failure may be caused by the
fact that under the default settings SQL Server does not allow remote
connections. (provider: SQL Network Interfaces, error: 28 – Server
doesn’t support requested protocol) (Microsoft SQL Server)”
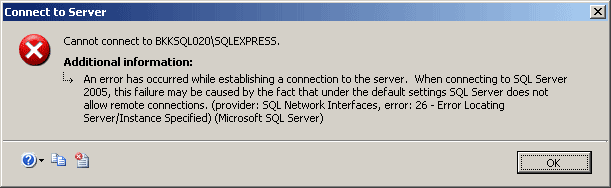
“Cannot connect to SQL-Server-Instance-Name
An error has occurred while establishing a connection to the server.
When connecting to SQL Server 2005, this failure may be caused by the
fact that under the default settings SQL Server does not allow remote
connections. (provider: SQL Network Interfaces, error: 26 – Error
Locating Server/Instance Specified) (Microsoft SQL Server)”
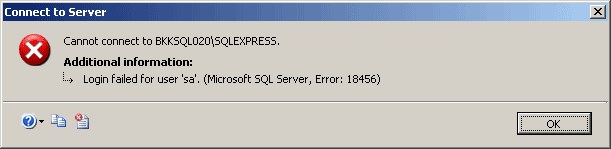
“Cannot connect to SQL-Server-Instance-Name
Login failed for user ‘username‘. (Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 18456)”
To enable remote connection on SQL Server
- Start SQL Server Browser service if it’s not started yet. SQL Server Browser listens for incoming requests for Microsoft SQL Server resources and provides information about SQL Server instances installed on the computer.
- Enable TCP/IP protocol for SQL Server 2008 to accept remote connection.
- (Optional)
Change Server Authentication to SQL Server and Windows Authentication. By default, SQL Server 2008 allows only Windows Authentication mode so you can connect to the SQL Server with current user log-on credential. If you want to specify user for connect to the SQL Server, you have to change Server Authentication to SQL Server and Windows Authentication.
Note: In SQL Server 2008 , there isn’t SQL Server Surface Area Configuration so you have to configure from SQL Server Configuration Manager instead.
Step-by-step
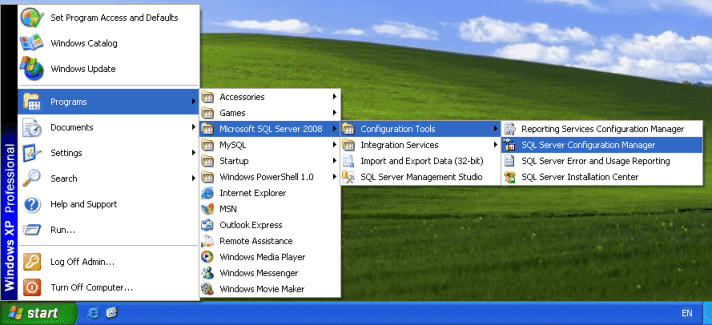
1- Open SQL Server Configuration Manager. Click Start -> Programs-> Microsoft SQL Server 2008 -> Configuration Tools -> SQL Server Configuration Manager.
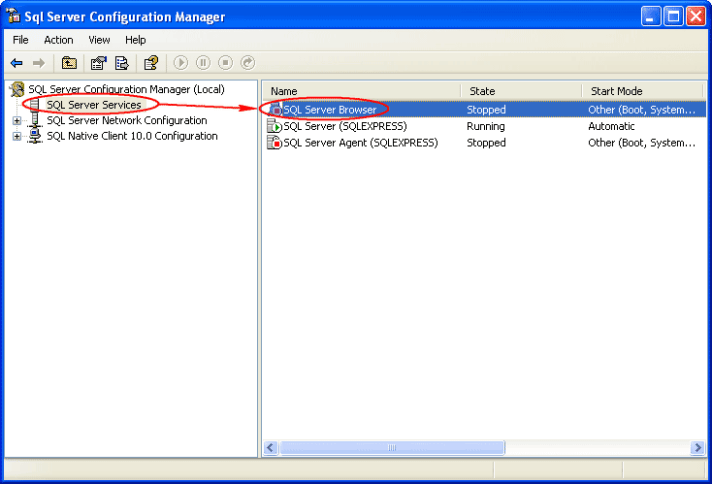
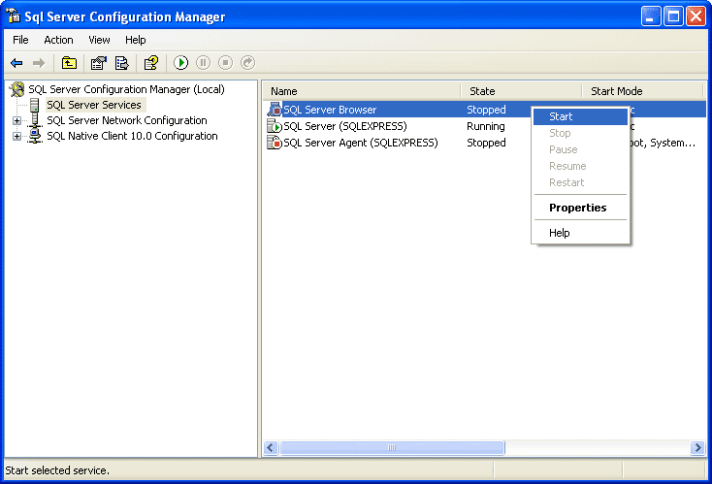
2- On SQL Server Configuration Manager, select SQL Server Services on the left window. If the state on SQL Server Browser is not running, you have to configure and start the service
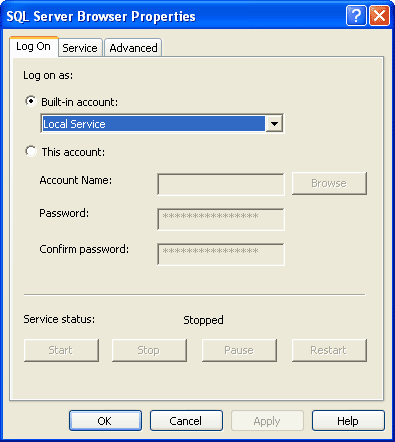
3- Double-click on SQL Server Browser, the Properties window will show up. Set the account for start SQL Server Browser Service. In this example, I set to Local Service account.
4- On SQL Server Browser Properties, move to Service tab and change Start Mode to Automatic. Therefore, the service will be start automatically when the computer starts. Click OK to apply changes.
5- Back to SQL Server Configuration Manager, right-click on SQL Server Bowser on the right window and select Start to start the service.
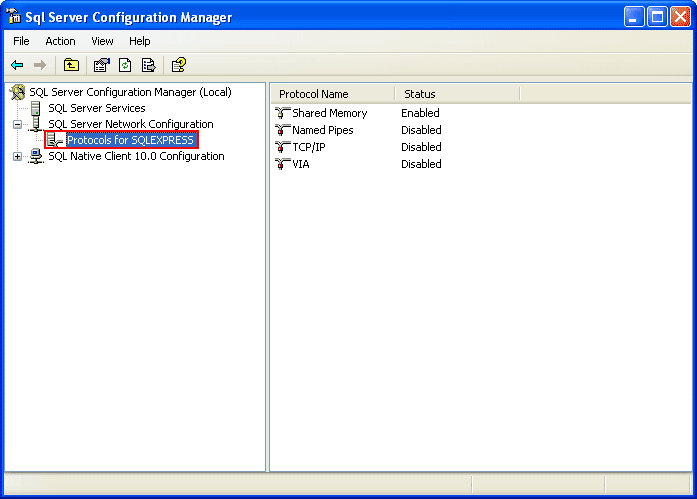
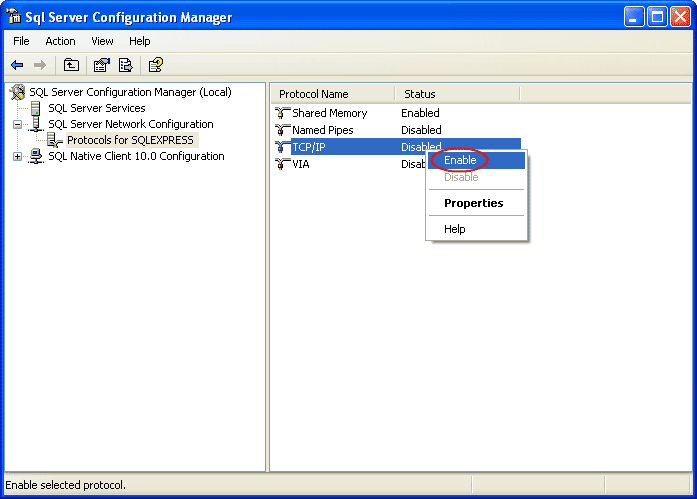
6-On the left window, expand SQL Server Network Configuration -> Protocols for SQLEXPRESS. You see that TCP/IP protocol status is disabled.
7- Right-click on TCP/IP and select Enable to enable the protocol.
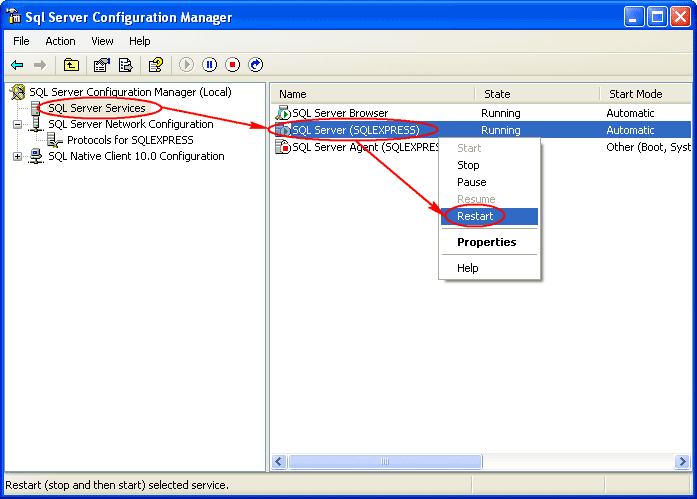
8- On the left window, select SQL Server Services. Select SQL Server (INSTANCE NAME) on the right window -> click Restart. The SQL Server service will be restarted.
9-Open Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio and connect to the SQL Server 2008 Express.
10- Right-click on the SQL Server Instance and select Properties.
11- On Server Properties, select Security on the left window. Then, select SQL Server and Windows Authentication mode.
12 -Right-click on the SQL Server Instance and select Restart.