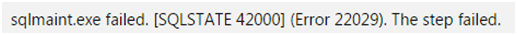Running DBCC CHECKDB you are getting following error message:
Check Catalog Msg 3853, State 1: Attribute (referenced_object_id=194099732,key_index_id=7) of row (object_id=2040565179) in sys.foreign_keys does not have a matching row (object_id=194099732,index_id=7) in sys.indexes
This error means, that Unique key constraint (index_id 7) in the primary table (object_id 194099732) is missing, which was referenced by child table’s FK constraint (FK object_id 2040565179). This should not happen, SQL Server will not allow you to drop a constraint that is referenced by FK. If attempted should get following error message:
Msg 3723, Level 16, State 6, Line 1
An explicit DROP INDEX is not allowed on index ‘dbo.a.NonClusteredIndex-20151119-085219’. It is being used for FOREIGN KEY constraint enforcement.
So if we are suppose to get errors? Why do we have corruption; simple answer, someone be making updates to system tables directly, which is not allowed or supported!
Actually we are not able to update system tables in SQL Server 2005+ (ref), however in SQL 2000 days, we had setting called allow updates in sp_configure options. Also supported by the KB2787112.
So question is how do you fix it?
First, identify the child table name from sys.foreign_keys:
SELECT object_name(parent_object_id) AS TableName
FROM sys.foreign_keys
WHERE name = ‘FK_b_a’
Second, script our constraint definition:
- Find the table, we got in SQL Statement above.
- Go to Keys.
- Right click on FK constraint name.
- Script Key As.
- Create To.
- New Query Window.
Third, drop the FK constraint:
ALTER TABLE [schema].[tablename] DROP CONSTRAINT [fk_constraint_name]
Fourth, Re-create the constraint, with script generated in Step 2.
If it was issue of someone playing around in system tables, this should resolve it. However, if you get error similar to below:
Msg 1776, Level 16, State 0, Line 1
There are no primary or candidate keys in the referenced table ‘dbo.a’ that match the referencing column list in the foreign key ‘FK_b_a’.
This means, that the key is missing in parent table and appropriate index needs be created before FK constraint can be created. Since SQL doesn’t allow the index to be dropped there most likely are other corruption issues that have gone unnoticed. If that is an issue, you will have to rely on your backups for recovery.
This post is cross posted on my SQLCAN Blog, MSDN Blog, and SQL server Consultation blog.